What’s the Difference between a Firewall and a VPN?
As firewall, VPN and antivirus are great tools to protect yourself from security issues on a network, there are absolutely not the same thing. In this article, we’ll especially take a look at how firewall and VPN differ.
As a general rule, a firewall protects an entry point to a network while a VPN secures the network flow between two points. Firewall are configured with a set of rules to filter the traffic, VPN create an encrypted tunnel between two networks.
This is the short answer, but we’ll now see both solutions in more details in the following. We’ll also compare them point per point at the end.
What is a Firewall
Definition
In computing, a firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
Wikipedia
As explained in the introduction, you can see a firewall as a software, configured to only let pass what is required for your normal network usage. Any forbidden traffic will be blocked at this point on the network.

Firewall basic example
Let’s take a basic example. At work, your company has probably configured a firewall a certain way.
In general, the configuration looks like this:
- Allow the minimum access to employees: web access, emails, maybe some FTP access or specific applications in the cloud
- Block any access from outside, except a few ones if needed (maybe remote access for some employees for example)
If you try to do anything else on your computer, it won’t work.
Let’s say you try to download your personal emails, play a game or start a conference call that is not allowed, you will be blocked.
This is a security measure enforced by the company network administrators to protect the network from undesired stuff.
How does a Firewall Work?
The firewall analyzes any packet passing over the network, and check their content and destination against its predefined security rules. If it’s not allowed, the packet is stopped directly, resulting in a network error for the user.
There are several types of network, but they all work with a predefined set of rules.
In general, everything is blocked by default, and the administrator configures which app, IP address and port are allowed.
But it’s also possible to configure them the other way, allowing everything except a few apps, IP or ports.
Firewall examples
Firewall can be found at different places, with different level of complexity. At home, you’ll find them on each computer but the most important is on your Internet router because it handles the entry point to your home network.
Companies generally have a big firewall between the Internet and the local network. They can also have firewalls between different local networks (for example, a Wi-Fi network may have to pass through the firewall to access any server resources).
In general, any computer includes a basic firewall in the main operating system. On Windows, Windows Defender is preinstalled and enabled by default, it will handle the basics, and you can configure it in the control panel.
It’s also possible to replace by a more powerful solution. You can find some of them on Amazon, that’s pretty cheap, and it’s effective to protect your data. These suites often include other security tools like Antivirus and Anti-malware.
What is a VPN
Definition
A virtual private network (VPN) extends a private network across a public network and enables users to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network
Wikipedia
To make this even clearer, a VPN is a bridge between two networks. When you exchange data with someone else over the Internet, your data goes in clear outside your network. There is a risk that someone can intercept your data in the middle. By using a VPN, your data is encrypted from your computer or network to the recipient, protecting it from any attack.
The three types of VPNs
There are three cases in which VPNs are generally used. The first is from your network to the Internet, to protect your browsing data. The second one is the opposite, to access a home or business network from the outside. The last one is to connect two sites together (mainly used by companies).
The first one is the most used by individual users at home. Famous providers like NordVPN offer a great solution for a few dollars each month to protect all your online activity. Your Internet usage will go through an encrypted tunnel between your computer and their servers, so that nobody can read your data in the middle.
It’s a great solution if you want to protect your personal data, but it’s also useful to bypass some country limitations as you can choose the server location you connect to. If you are in Europe, and choose a US server, you can then access websites as if you were in the United States (Netflix and Amazon Prime Video for example).
The two others are mostly used at work. For example, remote access allows sales people to access files on a local server in the company. And site-to-site connection are useful when a company has several buildings or subsidiaries, to safely connect them together.
How does a VPN works?
A VPN is generally built with two network points communicating together through an encrypted tunnel. Each point is configured similarly, allowing access from the other with the same security rules (IP, encryption method and security keys).
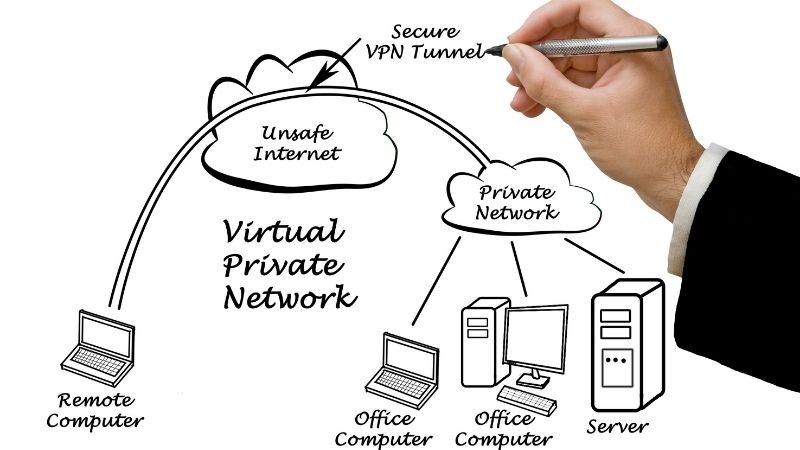
This technology disguises your IP address as you are seen on the Internet through the remote server, and it also makes sure you are the only one that can access the data. Even if an attacker intercept a packet from you, they will need the encryption technology and security key to read it.
Differences between a Firewall and a VPN
Goal
While firewall and VPN are two important security measures, they don’t have the same goal.
A firewall is set up to avoid forbidden access to any network content. It can protect a local network from remote attacks and also filter access inside a network or to the Internet.
A VPN doesn’t filter or block anything, it’s a safer way to communicate between two networks, either from your home computer and the Internet, from outside to a local network or even between two sites. The goal of a VPN is to avoid man-in-the-middle attacks.
Setup
A firewall is installed between two networks, it’s a connection point.
A VPN software is set up on the two points that need to be connected, it’s a link, a tunnel, not a specific point on the network.
Configuration
A firewall has a specific set of rules configured for each interface that connect it to a network. At home, there are generally two networks only (LAN and Internet), while companies can have dozens of sub-networks, all filtered by a unique firewall.
VPN are configured with the same security keys, encryption methods, and each of them know the IP address from the other network.
Comparison table
| Firewall | VPN | |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Specific point on the network | Link between two networks |
| Goal | Avoid network instrusions and filter allowed content | Encrypt data exchanged between to network to avoid interception |
| Configuration | Network administrators define a set of rules for allowed usage on their network | Network administrators configure the two points to link them together, with the same security configuration |






