DNS vs IP Address: The Secret Language of the Web Explained!
You have probably already heard about these terms: IP address and DNS, but now that you think about it, it’s not necessarily crystal clear how they play an important life in our hyper-connected life. Well, let me explain everything with simple words.
The main difference between IP addresses and DNS is that an IP address is a unique numerical identifier assigned to every device connected to a network, while DNS (Domain Name System) translates human-friendly domain names into IP addresses.
That’s the short answer to your question, but keep reading to better understand everything, I’ll give you examples and analogy in addition to the main definitions and roles.
What Is an IP Address?
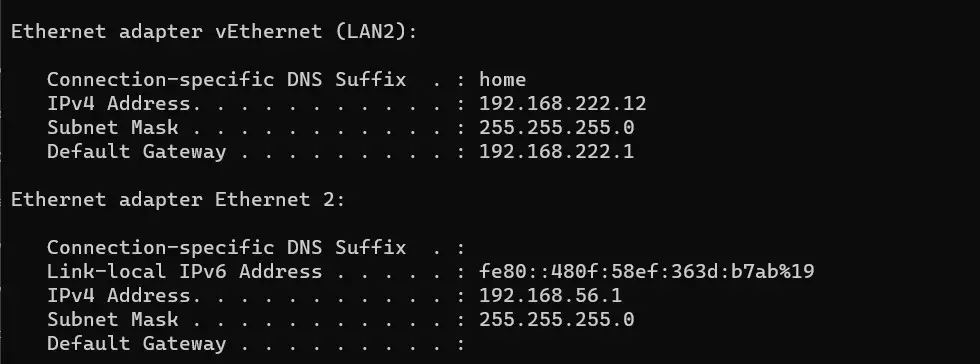
Definition of IP Address
An IP Address is like a phone number for your computer or any device connected to a network (Internet or local network). Every device needs this unique number to communicate with others.
Types of IP Addresses
There are two main types of IP addresses:
- IPv4 (e.g., 192.168.1.1): The older version, still widely used.
- IPv6 (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334): A newer, more complex version that’s becoming more common as the internet grows.
How IP Addresses Work
Just like how you dial a phone number to call someone, devices use IP addresses to reach each other. When you enter a website, your computer needs the IP address of that website’s server to access it and fetch the data you’re looking for (a webpage, for example).
Related: What’s the Difference Between IP Address and URL?
What Is DNS (Domain Name System)?
Definition of DNS
DNS, or Domain Name System, is like your phone’s contact list but for websites. Instead of remembering all the numbers, you just need to know the name.
When you want to use Google, you type the domain name (google.com) in your web browser, not the numeric IP address of the server hosting Google.
Purpose of DNS
The main purpose of DNS is to translate human-friendly domain names like “google.com” into the machine-readable IP addresses.
Related: What’s the Difference between DNS and DHCP?
How DNS Works
When you type in a web address, DNS translates that into the corresponding IP address, just like looking up a friend’s name in your contacts to find their number.
How Do IP Addresses and DNS Interact?
Connecting to Websites
DNS and IP addresses work together to connect you to websites. Think of it as using your contact list to dial a friend’s phone number.
Role of DNS in Translating Domain Names
Without DNS, you’d have to memorize every website’s IP address you wanted to visit. It’s a helpful system that takes care of this for us.
Common Examples
When you go to “youtube.com,” DNS translates it into the appropriate IP address, allowing your browser to connect to YouTube’s server.
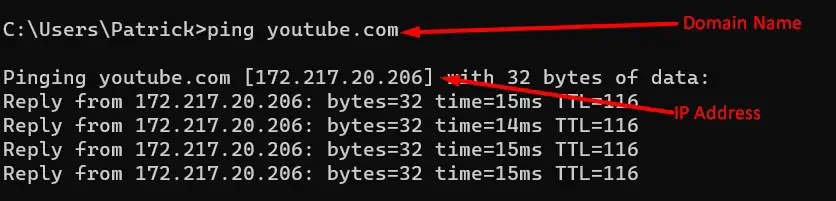
Why Do We Need Both IP Addresses and DNS?
Necessity of IP Addresses
Every device needs an IP address to communicate online, like having a unique phone number.
Importance of DNS
Without DNS, you’d have to remember all those numbers for each website. It acts as your digital phone book.
The Relationship Between Them
DNS translates the website names into IP addresses, and your computer uses these IP addresses to connect to the websites. It’s like using a phone book and then dialing the number.
Main Differences Between IP Address and DNS
Function and Purpose
IP Addresses are unique numbers for devices, while DNS translates domain names to these numbers.
Technical Composition
IP Addresses consist of numbers (and sometimes letters in IPv6), while DNS is a system that uses servers to translate domain names.
How They Work Together and Separately
IP Addresses are used by devices to connect with each other, while DNS helps humans navigate the web without memorizing all these numbers.
Comparison Table
| Feature | IP Address | DNS |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unique number for devices | Translates domain names to IPs |
| Function | Identifier for devices on a network | Helps humans navigate the web |
| Format | Generally numbers (but IPV6 has letters) | A server, set up in the network configuration of each device. |
| Link between them | Works with DNS to connect sites | Translates names to IPs |
| Necessity for Users | Required for device connection | Makes web browsing user-friendly |
Related Questions
What Is a Static IP Address?
A static IP address is one that doesn’t change. It’s like having a permanent phone number. Businesses often use static IP addresses because they’re consistent, which can be essential for certain functions.
How Does a DNS Server Work?
A DNS server acts as the manager of the phone book. When you type in a web address, the DNS server finds the right IP address for that domain, connecting your browser to the website.
Can I Change My IP Address?
Yes, you can change your IP address, but it’s usually not needed for everyday users. It’s akin to changing your phone number; you might do it for specific reasons, but most people keep the same number for convenience.
What Happens if DNS Fails?
If DNS fails, it’s like losing access to your contacts in your phone. You’d know the names but not the numbers. You could still access websites if you knew their IP addresses, but most people don’t, so many sites would become unreachable.