What’s the difference between MB and KB?
Language close to Chinese for the uninitiated, MB and KB are often misunderstood. I have done a lot of tech support in my life, and I can tell you that you’re not the only one in this case 🙂
No worries, I have the answers for you, here are the main difference between MB and KB:
Overall, MB and KB are units of measure for files, expressed in bytes. A kilobyte (KB) is equal to 1000 bytes, while a megabyte (MB) is equal to 1000 kilobytes or 1 million bytes. Basically, a 1 MB file is one thousand larger than a 1 KB file.
I will explain later the exact value, the other multiples that can serve you, and the difference with KiB/ MiB.
A byte
Definition
A unit of computer information or data-storage capacity that consists of a group of eight bits and that is used especially to represent an alphanumeric character
Merriam-Webster
Without going into more detail, the byte is the main unit of measure for computers and any device with a storage
Each file on your computer has a size in bytes
The file size depends on the amount of data inside it
And each storage device (hard disk, DVD, RAM, …) has a maximum size in bytes

- Back in the days, a floppy disk was 1.44 MB.
- A CD-ROM is around 700 MB.
- A standard DVD is generally a bit less than 5 GB (about 5,000 MB).
- USB sticks have different sizes, ranging from 8 GB to 128 GB in general.
- And hard drives (internal or external) go from 100 GB to 8 TB (8,000 GB).
You should also read: SIM Card vs SD Card: What’s the Difference?
Base 10 units
All of this will be simple if we had remained there, with very small storage media as at the beginning of the computer age
But this has quickly evolved, and we now need to use byte multiples: kilobyte, megabyte, gigabyte or terabyte
Multiples are simply the same as in any measuring system
1 kilometer = 1000 m, 1 kilobyte = 1000 bytes
I will give you the correlation table just after, but first I have to go back to the first problem of this notation.
Base 2 units
In this section, I will go deeper. I will also explain to you the difference between KB and KiB, or MB and MiB
Frankly, if you are new to this and understood the previous part, congrats, you already know more than 50% of computer users in the world 🙂
You can absolutely skip this part. But if you want to know more than 90% of users …. stay withe me!
Historically, kilobytes and megabytes were not measured in base 10 but in base 2
Until 1998, 1 kilobyte was 1024 bytes (2¹⁰)
To avoid this confusion (we’ll see another one later), base 2 units have been renamed to:
- KiB = kibibyte
- MiB = mebibyte
- GiB = gibibyte
Names are funny, but it creates many mistakes
This change is quite recent, you’ll probably see people or software that mixes KiB and KB
For example, Windows use GiB but hard drive manufactures use GB. That’s why you never get 500 GB of space available when you buy a hard drive
In everyday life this should not be a problem, the goal is rather to compare the values of the same system of notation between them (is 100Ko is greater than 1MB?), But two units will usually be the same
Correlation table
We’ll now see the correspondence table between units and values in bytes
This is helpful to compare the disk usage for two different files
To keep this simple, I’ll give you the table only in base 10, but it’s almost the same in base 2, or with other any units
| Unit | Multiple | Value in bytes |
| 1 KB (kilobyte) | 10³ (10×10×10) | 1,000 bytes |
| 1 MB (megabyte) | 10⁶ | 1,000,000 bytes or 1,000 KB |
| 1 GB (gigabyte) | 10⁹ | 1,000,000,000 bytes or 1,000 MB |
| 1 TB (terabyte) | 10¹² | 1,000,000,000,000 bytes or 1,000 GB |
To sump up, the only thing to remember is the unit order
Once you know the order KB < MB < GB < TB and each higher unit is 1000 times more than the lower, you know everything you need
On your computer you will often see files in KB or MB, so it’s even easier to start with only two units
Bits
Yes, I’m sorry, they also added the bits unit …
I can probably made another entire article with the difference between bytes and bits
But for the moment I will keep this simple, you already know what you need to know to answer your primary question
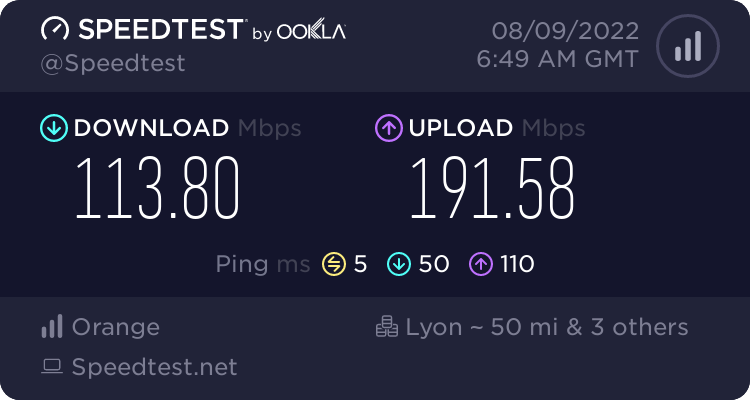
So, you can also find sometimes units in Kb, Mb, Gb, etc.
And the same story with Kib, Mib and Gib for base 2 values
Everything I explained for KB and KiB, work for Kb and Kib, so you won’t have any problem with this
Related questions
How to know the size of a file?
On Windows, you can see this at the bottom of the explorer when you select a file. You can also do a right-click on the file, then Properties, to get the information if needed.
You’ll have something similar on Linux and macOS.
Is KB smaller than MB?
A kilobyte (KB) is approximately 1,000 times smaller than a megabyte (MB).
How to convert MB to KB?
You can multiply the number of megabytes (MB) by 1,024 to get the corresponding number of kilobytes (KB).
You can also use an online converter to get it faster (Google search can do it natively too).
Conclusion
That’s it, you now know the difference between MB and KB and you can now work easily with these multiples in your next emails 🙂
I hope I didn’t get too confused with MiB, Mb and MB, but it’s not the most important, so if that’s the case you can forget this part