4 Essential Differences Between a Computer and a PC
When we are not very advanced about technology, we tend to mix different words that not necessarily mean the same thing. As a computer engineer, it tends to irritate me. But anyway, in this article I will try to make the difference between a computer and a PC clearer for you, so you can use the correct word in any situation.
As a whole, a PC or personal computer target a niche audience, to be used by individuals. Computer is a generic term that include PC but also other categories like servers and smartphones. In the early days, computer were not affordable for individuals, that’s why these two words still exist today.
Keep reading to learn all the details, and especially understand how the computer history play a role for these two words that seem similar today.
Users
One of the most significant differences between a computer and a PC is who the intended user is. The Personal Computer (PC) has a niche audience. It’s designed to be used by individuals. Usually, the owner will be the only person who uses the PC.
Sometimes, though, a personal computer can extend to being used by members of the same household. In this case, they will each be given their own username and password. While they will be sharing the device, they can each use it privately.
There are multiple types of PC, depending on the type of users. Some examples include:
- Desktop computer. This comes with a tower, which is where the computer is kept. For it to work, it will need to be connected to a monitor. If you’re curious about how this works, check out my article on the difference between a computer and a monitor.
- All-in-one computers. These are similar to desktops. But they combine a monitor and tower, so there is just one unit.
- Laptop. This is foldable and easier to transport.
- Two-in-one. This can be used as either a tablet or a laptop, because of a removable keyboard.
On the other hand, a computer will be connected to a wider network. For example, a business might have multiple computers, connecting them through a server. This allows all the other users to communicate and share data across the network.
A computer has a wider range of applications. Some examples include:
- Business. Today, a computer has become a necessity for most business operations. Even a local corner store will need to use a computer to keep track of inventory and deliveries.
- Government. The ability to store vast amounts of information has made the computer an essential choice for government organizations around the globe.
- Schools. As technology becomes more integrated into our lives, teaching children how to use it has become more important.
- Military. Computers are used for surveillance, analyzing data, and can even be used for warfare, like launching missiles.
- Tech companies. Institutions like Facebook and Google have thousands of computers, one for each of their employees.
Many of these users will have access to large banks of computers. It’s not uncommon for a university to have dozens available. Government organizations might have hundreds.
These types of computers also tend to be more advanced than what you would expect from a PC. For example, you might see a tech firm that has advanced servers, capable of storing huge amounts of data. This won’t be available for those in the PC market.
Most PCs will have limited computing power when compared to the massive computers available for larger organizations. However, they won’t need it. Most people are content with using their PC for more basic tasks. Some of the most popular options include:
- Writing documents
- Using spreadsheets
- Online shopping
- Browsing the internet
- Playing computer games
- Listening to music or watching movies
- Editing photos or videos
This is just the tip of the iceberg. There are thousands of apps that have been designed for the PC market. Though most will be fairly simple, to comply with the limited memory and processing power of a PC.
History
The computer has a long history. The first ideas for a computer stretch back to 1801, when a machine was created that used punch cards to create designs. From there, work on the computer continued. There were several notable names involved in its creation from Ava Lovelace to Alan Turing.
However, it wasn’t until 1946 that it started to come into the mainstream. The UNIVAC was designed to be used by businesses and governments to help them store data and perform calculations.
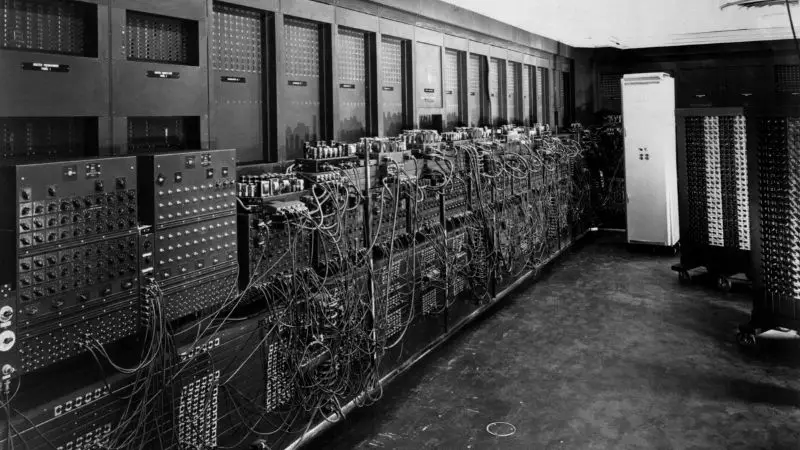
For a long time, though, the size of the machines meant that computers were only available to larger organizations and businesses. In the early days, a computer could take up a whole room. Even as the size of the computer started to shrink, they remained fairly expensive. This made it difficult for the average worker to afford.
Though computers had existed for decades prior, the first PC was released in 1981. It was known as the Acorn and was priced at over $1,000. Despite the high cost, its capabilities were fairly limited. Though, combined with products from Apple, home computing would become a possibility over the next few years.
Size of the Market
Over the years, the technology market has ballooned. This trend is only beginning, with a huge number of computers expected to be sold over the coming years. PCs are set to experience the most growth over the coming years.
Here are some of the industry projections:
- The market was worth $145 billion in 2020
- It rose to $161 billion in 2021
- It’s expected that the global PC market will be worth around $224 billion in 2025.
Unlike business computers, the cost of purchasing the computer will belong to the end-user. Because of this, there is a limit to how much people are willing to pay for a PC. Most will cost between $500 to $3,000.
However, the PC market is only a small proportion of the market for computers. As we mentioned, it doesn’t take into account users like the government, tech companies, or universities. These are some of the biggest markets for computers.
For example, Facebook is expected to spend between $29 to 34 billion in 2022 alone. This will include things like software, servers, and new data centers. This pales in comparison to the amount of money that the government plans to spend on technology. The U.S. government asked to spend $109 billion in 2022 on IT.
Control
The next thing to consider is the amount of control you will have over how the machine is being used. On a PC, the user will often have total control. You’ll be able to decide what type of programs you will be able to install and what operating system you use.
This is true of computers generally. Though they might come with a pre-installed operating system, you will be able to remove and replace it with another. You’ll just be limited to the system requirements.
It should be noted that when thinking about a PC, most people tend to think about Windows and exclude Macs. This is incorrect. Any type of operating system or computer size can become a PC. The key is how many people are using it. To be a PC, it can only be used by one user, rather than many people on a network.
However, if you are using the computer as part of your work, there will be limits to what you can do. Common restrictions include:
- Restrictions to what you can search for online
- Limited to what type of software you can use
- Difficult to install new apps
Only the network administrator will be able to install apps on work or business computers. They will need to enter a username and password. On a PC, you will still need to give permission. But you will be the only one who gets to decide what is being put on the computer. This gives you more freedom when you are using your PC.
However, there are some things that a computer can do that a PC can’t. On a computer, you’ll be able to connect with a larger network. Because of this, it will be easy to share documents. Some programs will require you to connect to the server before they will work.
Furthermore, some computers will have technical abilities that the average PC can’t replicate. For example, quantum computers are capable of solving some of the most advanced problems in the world. You won’t be able to get this same level of computing power from your computer at home.